
Research Topics
Publications on Unemployment
-
What Jobs Should a Public Job Guarantee Provide?
Working Paper No. 981 | January 2021Lessons from Hyman P. Minsky
The job guarantee is a viable policy option for tackling both unemployment and underemployment. Hyman P. Minsky was one of the seminal writers on this subject. The first part of this working paper provides a survey of Minsky’s writings to identify what kind of jobs he had in mind when recommending employer-of-last-resort policies. Minsky favored: (1) jobs increasing socially useful output, providing all of society better public services and goods; (2) jobs guaranteed by the public sector on a project-by-project basis at a minimum wage; (3) jobs in the places where people need them; and (4) jobs taking the people that need them as they are. The second part of the paper suggests policy recommendations for today’s economy. As long as the COVID-19 pandemic still rages on, a targeted public job guarantee program can assist in the social provisioning and distribution of food, shelter, and medical services. After the pandemic, a public job guarantee can reduce poverty and inequality, and bring about a more democratic, sustainable, and socially cohesive economic system.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Daniel Haim -
Guaranteeing Employment during the Pandemic and Beyond
Policy Note 2020/4 | May 2020The ongoing job losses, already numbering in the tens of millions, and the mass unemployment that will remain once the COVID-19 crisis has passed are of our own making, argues Pavlina R. Tcherneva, created by our inability to conceive of policies that protect and create jobs on demand. There is another option: instead of capitulating to a world of guaranteed unemployment, we can demand policies that guarantee employment. During the pandemic, the government can protect jobs by acting as a kind of employer of last resort, while in the post-pandemic world it can create jobs directly via mass mobilization and a job guarantee. In this environment, backstopping payrolls, mass mobilization, and the job guarantee are three different but organically linked policies that aim to secure the right to decent, useful, and remunerative employment opportunities for all.Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
The Job Guarantee
Working Paper No. 902 | April 2018Design, Jobs, and Implementation
The job guarantee (JG) is a public option for jobs. It is a permanent, federally funded, and locally administered program that supplies voluntary employment opportunities on demand for all who are ready and willing to work at a living wage. While it is first and foremost a jobs program, it has the potential to be transformative by advancing the public purpose and improving working conditions, people’s everyday lives, and the economy as a whole.
This working paper provides a blueprint for operationalizing the proposal. It addresses frequently asked questions and common concerns. It begins by outlining some of the core propositions in the existing literature that have motivated the JG proposal. These propositions suggest specific design and implementation features. (Some questions are answered in greater detail in appendix III). The paper presents the core objectives and expected benefits of the program, and suggests an institutional structure, funding mechanism, and project design and administration.Download:Associated Programs:Author(s): -
Unemployment: The Silent Epidemic
Working Paper No. 895 | August 2017This paper examines two key aspects of unemployment—its propagation mechanism and socioeconomic costs. It identifies a key feature of this macroeconomic phenomenon: it behaves like a disease. A detailed assessment of the transmission mechanism and the existing pecuniary and nonpecuniary costs of unemployment suggests a fundamental shift in the policy responses to tackling joblessness. To stem the contagion effect and its outsized social and economic impact, fiscal policy can be designed around two criteria for successful disease intervention—preparedness and prevention. The paper examines how a job guarantee proposal uniquely meets those two requirements. It is a policy response whose merits include much more than its macroeconomic stabilization features, as discussed in the literature. It is, in a sense, a method of inoculation against the vile effects of unemployment. The paper discusses several preventative features of the program.
Download:Associated Programs:Author(s): -
The Concert of Interests in the Age of Trump
Policy Note 2017/2 | July 2017If the Trump administration is to fulfill its campaign promises to this age’s “forgotten” men and women, Director of Research Jan Kregel argues, it should embrace the broader lesson of the 1930s: that government regulation and fiscal policy are crucial in addressing changes in the economic and financial structure that have exacerbated the problems faced by struggling communities.
In this policy note, Kregel explains how overcoming the economic and financial challenges we face today, just as in the 1930s, requires avoiding what Walter Lippmann identified as an “obvious error”: the blind belief that reducing regulation and the role of government will somehow restore a laissez-faire market liberalism that never existed and is inappropriate to the changing structure of production of both the US and the global economy.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Jan Kregel -
Full Employment: Are We There Yet?
Public Policy Brief No. 142, 2017 | February 2017Flavia Dantas and L. Randall Wray argue that the emerging conventional wisdom—that the US economy has reached full employment—is flawed. The unemployment rate is not providing an accurate picture of the health of the labor market, and the common narrative attributing shrinking labor force engagement to aging demographics is overstated. Instead, falling prime-age participation rates are the symptom of a structural inadequacy of aggregate demand—a problem of insufficient job creation and stagnant incomes that conventional public policy remedies have been unable to address. The solution to our long-running secular stagnation requires targeted, direct job creation for those at the bottom of the income scale.
-
Greece: Getting Out of the Recession
Strategic Analysis, September 2016 | October 2016The Greek government has agreed to a new round of fiscal austerity measures consisting of a sharp increase in taxes on income and property and further reductions in pension and other welfare-related expenditures. Based on our model of the Greek economy, policies aimed at reducing the government deficit will cause a recession, unless other components of aggregate demand increase enough to more than offset the negative impact of fiscal austerity on output and employment.
In this report we argue that the troika strategy of increasing net exports to restart the economy has failed, partly because of the low impact of falling wages on prices, partly because of the low trade elasticities with respect to prices, and partly because of other events that caused a sharp reduction in transport services, which used to be Greece’s largest export sector.
A policy initiative to boost aggregate demand is urgently needed, now more than ever. We propose a fiscal policy alternative based on innovative financing mechanisms, which could trigger a boost in confidence that would encourage renewed private investment.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
The Narrow Path for Brazil
Policy Note 2016/2 | April 2016Brazil is mired in a joint economic and political crisis, and the way out is unclear. In 2015 the country experienced a steep contraction of output alongside elevated inflation, all while the fallout from a series of corruption scandals left the policymaking apparatus paralyzed. Looking ahead, implementing a policy strategy that has any hope of addressing the Brazilian economy’s multilayered problems would make serious demands on a political system that is most likely unable to bear it.
-
What We Could Have Learned from the New Deal in Confronting the Recent Global Recession
Public Policy Brief No. 141, 2016 | March 2016To the extent that policymakers have learned anything at all from the Great Depression and the policy responses of the 1930s, the lessons appear to have been the wrong ones. In this public policy brief, Director of Research Jan Kregel explains why there is still a great deal we have to learn from the New Deal. He illuminates one of the New Deal’s principal objectives—quelling the fear and uncertainty of mass unemployment—and the pragmatic, experimental process through which the tool for achieving this objective—directed government expenditure—came to be embraced.
In the search for a blueprint from the 1930s, Kregel suggests that too much attention has been paid to the measures deployed to shore up the banking system, and that the approaches underlying the emergency financial policy measures of the recent period and those of the 1930s were actually quite similar. The more meaningful divergence between the 1930s and the post-2008 policy response, he argues, can be uncovered by comparing the actions that were taken (or not taken, as the case may be) to address the real sector of the economy following the resolution of the respective financial crises.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Jan Kregel -
A Complementary Currency and Direct Job Creation Hold the Key to Greek Recovery
One-Pager No. 52 | January 2016Even under optimistic assumptions, the policy status quo being enforced in Greece cannot be relied upon to help recover lost incomes and employment within any reasonable time frame. And while a widely discussed public investment program funded by European institutions would help, a more innovative, better-targeted solution is required to address Greece’s protracted unemployment crisis: an “employer of last resort” (ELR) plan offering paid work in public projects, financed by issuing a nonconvertible “fiscal currency”—the Geuro.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
How Long Before Growth and Employment Are Restored in Greece?
Strategic Analysis, January 2016 | January 2016The Greek economy has not succeeded in restoring growth, nor has it managed to restore a climate of reduced uncertainty, which is crucial for stabilizing the business climate and promoting investment. On the contrary, the new round of austerity measures that has been agreed upon implies another year of recession in 2016.
After reviewing some recent indicators for the Greek economy, we project the trajectory of key macroeconomic indicators over the next three years. Our model shows that a slow recovery can be expected beginning in 2017, at a pace that is well below what is needed to alleviate poverty and reduce unemployment. We then analyze the impact of a public investment program financed by European institutions, of a size that is feasible given the current political and economic conditions, and find that, while such a plan would help stimulate the economy, it would not be sufficient to speed up the recovery. Finally, we revise our earlier proposal for a fiscal stimulus financed through the emission of a complementary currency targeted to job creation. Our model shows that such a plan, calibrated in a way that avoids inflationary pressures, would be more effective—without disrupting the targets the government has agreed upon in terms of its primary surplus, and without reversing the improvement in the current account.Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Why Minsky Matters: An Introduction to the Work of a Maverick Economist
Book Series, November 2015 | November 2015By L. Randall Wray

Perhaps no economist was more vindicated by the global financial crisis than Hyman P. Minsky (1919–1996). Although a handful of economists raised alarms as early as 2000, Minsky’s warnings began a half century earlier, with writings that set out a compelling theory of financial instability. Yet even today he remains largely outside mainstream economics; few people have a good grasp of his writings, and fewer still understand their full importance. Why Minsky Matters makes the maverick economist’s critically valuable insights accessible to general readers for the first time. Author L. Randall Wray shows that by understanding Minsky we will not only see the next crisis coming but we might be able to act quickly enough to prevent it.
As Wray explains, Minsky’s most important idea is that “stability is destabilizing”: to the degree that the economy achieves what looks to be robust and stable growth, it is setting up the conditions in which a crash becomes ever more likely. Before the financial crisis, mainstream economists pointed to much evidence that the economy was more stable, but their predictions were completely wrong because they disregarded Minsky’s insight. Wray also introduces Minsky’s significant work on money and banking, poverty and unemployment, and the evolution of capitalism, as well as his proposals for reforming the financial system and promoting economic stability.
A much-needed introduction to an economist whose ideas are more relevant than ever, Why Minsky Matters is essential reading for anyone who wants to understand why economic crises are becoming more frequent and severe—and what we can do about it.
Published by: Princeton
-
Losing Ground
Policy Note 2015/7 | November 2015Demographic Trends in US Labor Force Participation
US labor force participation has continued to fall in the wake of the Great Recession. Improvements in the US unemployment rate reflect the fact that more people are falling out of the labor force, not a stronger labor market. Controlling for changes in the demographic makeup of the workforce (i.e., gender, age, education, and race), Research Scholar Fernando Rios-Avila investigates trends in labor force participation across and within groups between 1989 and 2013. He finds that not all groups have lost ground equally, while participation rates for some groups have actually increased. Understanding these patterns in labor force participation is a necessary first step toward crafting effective policy responses.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Time Use of Parents in the United States
Working Paper No. 812 | August 2014What Difference Did the Great Recession Make?
Feminist and institutionalist literature has challenged the “Mancession” narrative of the 2007–09 recession and produced nuanced and gender-aware analyses of the labor market and well-being outcomes of the recession. Using American Time Use Survey (ATUS) data for 2003–12, this paper examines the recession’s impact on gendered patterns of time use over the course of the 2003–12 business cycle. We find that the gender disparity in paid and unpaid work hours followed a U-shaped pattern, narrowing during the recession and widening slightly during the jobless recovery. The change in unpaid work disparity was smaller than that in paid work, and was short-lived. Consequently, mothers’ total workload increased under the hardships of the Great Recession and declined only slightly during the recovery.
-
Heterogeneity in the Relationship between Unemployment and Subjective Well-Being
Working Paper No. 808 | June 2014A Quantile Approach
Unemployment has been robustly shown to strongly decrease subjective well-being (or “happiness”). In the present paper, we use panel quantile regression techniques in order to analyze to what extent the negative impact of unemployment varies along the subjective well-being distribution. In our analysis of British Household Panel Survey data (1996–2008) we find that, over the quantiles of our subjective well-being variable, individuals with high well-being suffer less from becoming unemployed. A similar but stronger effect of unemployment is found for a broad mental well-being variable (GHQ-12). For happy and mentally stable individuals, it seems their higher well-being acts like a safety net when they become unemployed. We explore these findings by examining the heterogeneous unemployment effects over the quantiles of satisfaction with various life domains.
-
Dead Economic Dogmas Trump Recovery: The Continuing Crisis in the Eurozone Periphery
Public Policy Brief No. 133, 2014 | May 2014The “happy talk” emanating from eurozone officials regarding the economic crises in the periphery deserves some vigorous pushback. Focusing on the four bailed-out countries of Greece, Ireland, Portugal, and Spain, Research Associate and Policy Fellow C. J. Polychroniou argues in this policy brief that, contrary to the burgeoning optimism in official communications, these countries’ economies are still not on track for vigorous, sustainable recoveries in growth and employment—and that there is nothing surprising in this result.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):C. J. Polychroniou -
A New “Lehman Moment,” or Something Worse?
Policy Note 2013/9 | October 2013A Scenario of Hitting the Debt Ceiling
The United States entered the second week of a government shutdown on Monday, with no end to the deadlock in sight. The cost to the government of a similar shutdown in 1995–96 amounted to $2.1 billion in today’s dollars. However, the cost and broader consequences of today’s shutdown are not yet clear—especially since the US economy is in the midst of an anemic recovery from the biggest economic crisis of the last eight decades.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Fiscal Sadism and the Farce of Deficit Reduction in Greece
One-Pager No. 43 | September 2013Unemployment in Greece has climbed to a new record of 27.9 percent and the country is headed toward a third bailout. The obsession with reducing the budget deficit is crippling the Greek economy. Extreme fiscal consolidation in the midst of a major depression can only have extreme effects on output, leading to greater unemployment, widening poverty, massive loss of faith in political and social institutions, and the potential for political violence. This is precisely what has been taking place in Greece since 2010, as fiscal brutality intensifies from one year to the next. Offering Greece yet another bailout package is not the answer.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):C. J. Polychroniou -
A Failure by Any Other Name
Policy Note 2013/6 | July 2013The International Bailouts of Greece
Research Associate and Policy Fellow C. J. Polychroniou argues that a political solution based on a new economic vision is needed to bring an end to the Greek crisis. Polychroniou observes that what began as a financial crisis has been transformed into a full-fledged economic and social crisis by the neoliberal policies of the International Monetary Fund and the European Union (EU). Instead of growth, these policies have destroyed Greece’s economy, divided the eurozone states, and hobbled a fragile global recovery. The past six years have seen Greece’s descent into economic and social ruin. Exiting the current crisis, for Greece and countries throughout the eurozone, requires more than an end to austerity. Broadly, EU institutions must be radically restructured around the principles of sustainable, equitable growth. Specifically, Greece needs a comprehensive development plan, with massive public spending and investment.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):C. J. Polychroniou -
Is the Link between Output and Jobs Broken?
Strategic Analysis, March 2013 | March 2013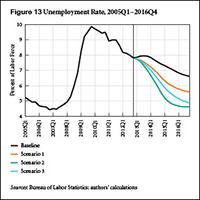
As this report goes to press, the official unemployment rate remains tragically elevated, compared even to rates at similar points in previous recoveries. The US economy seems once again to be in a “jobless recovery,” though the unemployment rate has been steadily declining for years. At the same time, fiscal austerity has arrived, with the implementation of the sequester cuts, following tax increases and the ending of emergency extended unemployment benefits just two months ago.
Our new report provides medium-term projections of employment and economic growth under four different scenarios. The baseline scenario starts by assuming the same growth rates and government deficits as the Congressional Budget Office’s (CBO) baseline projection from earlier this year. The result is a new surge of the unemployment rate to nearly 8 percent in the third quarter of this year, followed by a very gradual new recovery. Scenarios 1 and 2 seek to reach unemployment-rate goals of 6.5 percent and 5.5 percent, respectively, by the end of next year, using new fiscal stimulus.
We find in these simulations that reaching the goals requires large amounts of fiscal stimulus, compared to the CBO baseline. For example, in order to reach 5.5 percent unemployment in 2014, scenario 2 assumes 11 percent growth in inflation-adjusted government spending and transfers, along with lower taxes.
As an alternative, scenario 3 adds an extra increase to growth abroad and to private borrowing, along with the same amount of fiscal stimulus as in scenario 1. In this last scenario of the report, the unemployment rate finally pierces the 5.5 percent threshold from the previous scenario in the third quarter of 2015. We conclude with some thoughts about how such an increase in demand from all three sectors—government, private, and external—might be realistically obtained.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Current Prospects for the Greek Economy
Research Project Report, October 18, 2012 | October 2012Interim Report
In this interim report, we discuss the evolution of major macroeconomic variables for the Greek economy, focusing in particular on the sources of growth before and after the euro era, the causes and consequences of the continuing recession, and the likely results of the policies currently being implemented. Some preliminary suggestions for alternative policies are included. These alternatives will be tested in a more robust econometric framework in a subsequent report.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Time Use of Mothers and Fathers in Hard Times
Working Paper No. 726 | June 2012The US Recession of 2007–09
The recession precipitated by the US financial crisis of 2007 accelerated the convergence of women’s and men’s employment rates, as men experienced disproportionate job losses and women’s entry into the labor force gathered pace. Using the American Time Use Survey (ATUS) data for 2003–10, this study examines whether the recession also occasioned a decline in disparity in unpaid work burdens and provided impetus for overall progress toward equity in the workloads, leisure time, and personal care hours of mothers and fathers. Controlling for the prerecession trends, we find that the recession contributed to the convergence of both paid and unpaid work only during the December 2007–June 2009 period. The combined effect of the recession and the jobless recovery was a move toward equity in the paid work hours of mothers and fathers, a relative increase in the total workload of mothers, and a relative decline in their personal care and leisure time.
-
Neo-Hooverian Policies Threaten to Turn Europe into an Economic Wasteland
Policy Note 2012/1 | March 2012We live in a terrifying world of policymaking—an age of free-market dogmatism where the economic ideology is fundamentally flawed. Europe’s political leadership has applied neo-Hooverian (scorched-earth) policies that are shrinking economies and producing social misery as a result of massive unemployment.
Large-scale government intervention is critical in reviving an economy, but the current public-policy mania, which imposes fiscal tightening in the midst of recession, can only lead to catastrophic failure. The bailouts, for example, do not solve Greece’s debt crisis but simply postpone an official default. What is needed is a political and economic revolution that includes a return to Keynesian measures and a new institutional architecture—a United States of Europe.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):C. J. Polychroniou -
EU’s Anorexic Mindset Drives the Region’s Economies into Depression
One-Pager No. 27 | February 2012The coordinated contractionary policy on the part of the European Union is inspired by its belief that this is the most effective way to tackle the eurozone’s “debt crisis.” However, by ignoring the endemic problems of unemployment, poverty, and homelessness—all of which have as their underlying cause the contraction of economic activity—European economic policy reveals a growing gap with the real world.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):C. J. Polychroniou -
Is the Recovery Sustainable?
Strategic Analysis, December 2011 | December 2011Fiscal austerity is now a worldwide phenomenon, and the global growth slowdown is highly unfavorable for policymakers at the national level. According to our Macro Modeling Team's baseline forecast, fears of prolonged stagnation and a moribund employment market are well justified. Assuming no change in the value of the dollar or interest rates, and deficit levels consistent with the Congressional Budget Office’s most recent “no-change” scenario, growth will remain very weak through 2016 and unemployment will exceed 9 percent.
In an alternate scenario, the authors simulate the effect of new austerity measures that are commensurate with the implementation of large federal budget cuts. Here, growth falls to 0.06 percent in the second quarter of 2014 before leveling off at approximately 1 percent and unemployment rises to 10.7 percent by the end of 2016. In their fiscal stimulus scenario, real GDP growth increases very quickly, unemployment declines to 7.2 percent, and the US current account balance reaches 1.9 percent by the end of 2016—with a debt-to-GDP ratio that, at 97.4 percent, is only slightly higher than in the baseline scenario.
An export-led growth strategy may accomplish little more than drawing a small number of scarce customers away from other exporting nations, and the authors expect no net contribution to aggregate demand growth from the financial sector. A further fiscal stimulus is clearly in order, they say, but an ill-timed round of fiscal austerity could result in a perilous situation for Washington.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Time Use of Mothers and Fathers in Hard Times and Better Times
Working Paper No. 696 | November 2011The US Business Cycle of 2003–10
The US economic crisis and recession of 2007–09 accelerated the convergence of women’s and men’s employment rates as men experienced disproportionate job losses and women’s entry into the labor force gathered pace. Using the American Time Use Survey (ATUS) data for 2003–10, this study examines whether the narrowing gap in paid work over this period was mirrored in unpaid work, personal care, and leisure time. We find that the gender gap in unpaid work followed a U-pattern, narrowing during the recession but widening afterward. Through segregation analysis, we trace this U-pattern to the slow erosion of gender segregation in housework and, through a standard decomposition analysis of time use by employment status, show that this pattern was mainly driven by movement toward gender-equitable unpaid hours of women and men with the same employment status. In addition, gender inequality in leisure time increased over the business cycle.
-
Estimating the Impact of the Recent Economic Crisis on Work Time in Turkey
Working Paper No. 686 | September 2011This paper provides estimates of the impact of the recent economic crisis on paid and unpaid work time in Turkey. The data used in this study come from the first and only time-use survey available at the national level. Infrequency of collection of time-use data in Turkey does not allow us to make a direct comparison of pre- versus postcrisis time-use patterns. We introduce a tractable way for estimating these possible effects by measuring the impact of an increase in unemployment risk on time-use patterns of women and men living in couple households. The method developed here can be applied to other developing-country cases where there is a lack of longitudinal data availability. Our findings support the argument that economic crises reinforce the preexisting gender inequalities in work time.
-
Did Problems with SSDI Cause the Output-Jobs Disconnect?
One-Pager No. 9 | May 2011The slow recovery of the job market after the recessions of 2001 and 2007–09 has fostered concerns that the link between output growth and job creation has been severed. Between 2000 and 2010, the employment rate for males plunged from 71.9 to 63.7 percent—a decline that can be accounted for almost entirely by a fall in the employment rate for the disabled members of this group.
Research Scholar Greg Hannsgen examines whether the Great Recession disproportionately affected the job prospects of disabled workers, and whether the long-run fall in employment among the disabled can be blamed largely on the design of Social Security disability insurance. His findings? At least since 2008, the ongoing fall in the probability of being employed has strongly affected the job prospects of both the disabled and the nondisabled, and the accelerated declines since 2007 hint at an important, and negative, role for the recent recession. Hence, a government jobs initiative such as an employer-of-last-resort program, and not just long-term improvements in entitlement programs, is still very much apropos.
-
The Freedom Budget at 45
Working Paper No. 668 | May 2011Functional Finance and Full Employment
Forty-five years ago, the A. Philip Randolph Institute issued “The Freedom Budget,” in which a program for economic transformation was proposed that included a job guarantee for everyone ready and willing to work, a guaranteed income for those unable to work or those who should not be working, and a living wage to lift the working poor out of poverty. Such policies were supported by a host of scholars, civic leaders, and institutions, including the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.; indeed, they provided the cornerstones for King’s “Poor Peoples’ Campaign” and “economic bill of rights.”
This paper proposes a “New Freedom Budget” for full employment based on the principles of functional finance. To counter a major obstacle to such a policy program, the paper includes a “primer” on three paradigms for understanding government budget deficits and the national debt: the deficit hawk, deficit dove, and functional finance perspectives. Finally, some of the benefits of the job guarantee are outlined, including the ways in which the program may serve as a vehicle for a variety of social policies.
Download:Associated Programs:Author(s): -
Will the Recovery Continue?
Public Policy Brief No. 118, 2011 | April 2011Four Fragile Markets, Four Years Later
In this brief, Research Scholar Greg Hannsgen and President Dimitri B. Papadimitriou focus on the risks and possibilities ahead for the US economy. Using a Keynesian approach and drawing from the commentary of other observers, they analyze publicly available data in order to assess the strength and durability of the expansion that probably began in 2009. They focus on four broad groups of markets that have shown signs of stress for the last several years: financial markets, markets for household goods and services, commodity markets, and labor markets. This kind of analysis does not yield numerical forecasts but it can provide important clues about the short-term outlook for the country’s economic well-being, and cast light on some longer-run threats. In particular, dangers and stresses in the financial and banking systems are presently very serious, and labor market data show every sign of a widespread and severe weakness in aggregate demand. Unless there is new resolve for effective government action on the jobs front, drastic cuts in much-needed federal, state, and local programs will become the order of the day in the United States, as in much of Europe.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Jobless Recovery Is No Recovery: Prospects for the US Economy
Strategic Analysis, March 2011 | March 2011The US economy grew reasonably fast during the last quarter of 2010, and the general expectation is that satisfactory growth will continue in 2011–12. The expansion may, indeed, continue into 2013. But with large deficits in both the government and foreign sectors, satisfactory growth in the medium term cannot be achieved without a major, sustained increase in net export demand. This, of course, cannot happen without either a cut in the domestic absorption of US goods and services or a revaluation of the currencies of the major US trading partners.
Our policy message is fairly simple, and one that events over the years have tended to vindicate. Most observers have argued for reductions in government borrowing, but few have pointed out the potential instabilities that could arise from a growth strategy based largely on private borrowing—as the recent financial crisis has shown. With the economy operating at far less than full employment, we think Americans will ultimately have to grit their teeth for some hair-raising deficit figures, but they should take heart in recent data showing record-low “core” CPI inflation—and the potential for export-led growth to begin reducing unemployment.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Getting Out of the Recession?
Strategic Analysis, March 2010 | March 2010Research Scholar Gennaro Zezza updates the Levy Institute’s previous Strategic Analysis (December 2009) and finds that the 2009 increase in public sector aggregate demand was a result of the fiscal stimulus, without which the recession would have been much deeper. He confirms that strong policy action is required to achieve full employment in the medium term, including a persistently high government deficit in the short term. This implies a growing public debt, which is sustainable as long as interest rates are kept at the current low level. The alternative is an ongoing unemployment rate above 10 percent that would represent a higher cost to future generations.Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Sustaining Recovery: Medium-term Prospects and Policies for the US Economy
Strategic Analysis, December 2009 | December 2009Though recent market activity and housing reports give some warrant for optimism, United States economic growth was only 2.8 percent in the third quarter, and the unemployment rate is still very high. In their new Strategic Analysis, the Levy Institute’s Macro-Modeling Team project that high unemployment will continue to be a problem if fiscal stimulus policies expire and deficit reduction efforts become the policy focus. The authors—President Dimitri B. Papadimitriou and Research Scholars Greg Hannsgen and Gennaro Zezza—argue that continued fiscal stimulus is necessary to reduce unemployment. The resulting federal deficits would be sustainable, they say, as long as they were accompanied by a coordinated and gradual devaluation of the dollar, especially against undervalued Asian currencies—a step necessary to prevent an increase in the current account deficit and ward off the risk of a currency crash.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Lessons from the New Deal
Working Paper No. 581 | October 2009Did the New Deal Prolong or Worsen the Great Depression?
Since the current recession began in December 2007, New Deal legislation and its effectiveness have been at the center of a lively debate in Washington. This paper emphasizes some key facts about two kinds of policy that were important during the Great Depression and have since become the focus of criticism by new New Deal critics: (1) regulatory and labor relations legislation, and (2) government spending and taxation. We argue that initiatives in these policy areas probably did not slow economic growth or worsen the unemployment problem from 1933 to 1939, as claimed by a number of economists in academic papers, in the popular press, and elsewhere. To substantiate our case, we cite some important economic benefits of New Deal–era laws in the two controversial policy areas noted above. In fact, we suggest that the New Deal provided effective medicine for the Depression, though fiscal policy was not sufficiently countercyclical to conquer mass unemployment and prevent the recession of 1937–38; 1933’s National Industrial Recovery Act was badly flawed and poorly administered, and the help provided by the National Labor Relations Act of 1935 came too late to have a big effect on the recovery.
Download:Associated Programs:Author(s): -
The Current Economic and Financial Crisis
Working Paper No. 562 | May 2009A Gender Perspective
Widespread economic recessions and protracted financial crises have been documented as setting back gender equality and other development goals in the past. In the midst of the current global crisis—often referred to as “the Great Recession”—there is grave concern that progress made in poverty reduction and women’s equality will be reversed. Indeed, for many developing countries it is particularly worrisome that, through no fault of their own, the global economic downturn has exacerbated effects from other crises manifest in food insecurity, poverty, and increasing inequality. This paper explores both well-known and less discussed paths of transmission through which crises affect women’s world of work and overall wellbeing. As demand for textile and agricultural exports decline, along with tourism, job losses are expected to rise in these female-intensive industries. In addition, the gendered nature of the world of work suggests that women will see an increase in their share among informal and vulnerable workers worldwide, and will also supply more of their labor under unpaid conditions. The latter is particularly important in the context of developing countries, where many production activities take place outside the strict boundaries of the market. The paper also makes this point: examined through the prism of gender equality, the ability of the state to implement countercyclical policies matters greatly. If policy responses at the national and international levels end up aggravating inequities, gender equality processes face many more barriers, especially among the poor.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
The Social and Economic Importance of Full Employment
Working Paper No. 560 | April 2009Unemployment was singled out by John Maynard Keynes as one of the principle faults of capitalism; the other is excessive inequality. Obviously, there is some link between these two faults: since most people living in capitalist economies must work for wages as a major source of their incomes, the inability to obtain a job means a lower income. If jobs can be provided to the unemployed, inequality and poverty will be reduced—although such policy will not directly address the problem of excessive income at the top of the distribution. Most importantly, Keynes wanted to put unemployed labor to work—not digging holes, but in socially productive ways. This would help to ensure that the additional effective demand created by government spending would not be exhausted in higher prices as it ran up against bottlenecks or other supply constraints. Further, it would help maintain public support for the government’s programs by providing useful output. And it would generate respect for, and feelings of self-worth in, the workers employed in these projects (no worker would want to spend her days digging holes that serve no useful purpose). President Roosevelt’s New Deal jobs programs (such as the Works Progress Administration and the Civilian Conservation Corps) are good examples of such targeted job-creating programs. These provided income and employment for workers, actually helped increase the nation’s productivity, and left us with public buildings, dams, trails, and even music that we still enjoy today. As our nation (and the world) collapses into deep recession, or even depression, it is worthwhile to examine Hyman P. Minsky’s comprehensive approach to resolving the unemployment problem.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Flow of Funds Figures Show the Largest Drop in Household Borrowing in the Last 40 Years
Strategic Analysis, January 2009 | January 2009The Federal Reserve’s latest flow-of-funds data reveal that household borrowing has fallen sharply lower, bringing about a reversal of the upward trend in household debt. According to the Levy Institute’s macro model, a fall in borrowing has an immediate effect—accounting in this case for most of the 3 percent drop in private expenditure that occurred in the third quarter of 2008—as well as delayed effects; as a result, the decline in real GDP and accompanying rise in unemployment may be substantial in coming quarters.
For further details on the Macro-Modeling Team’s latest projections, see the December 2008 Strategic Analysis Prospects for the US and the World: A Crisis That Conventional Remedies Cannot Resolve.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):
